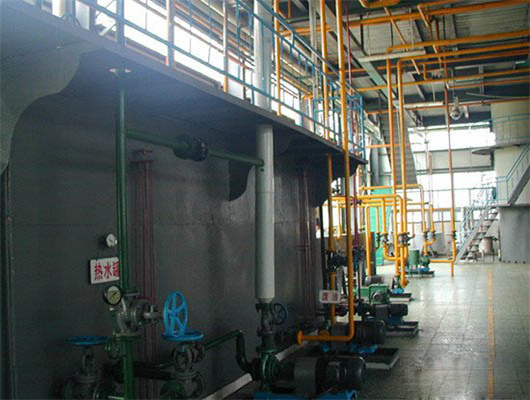
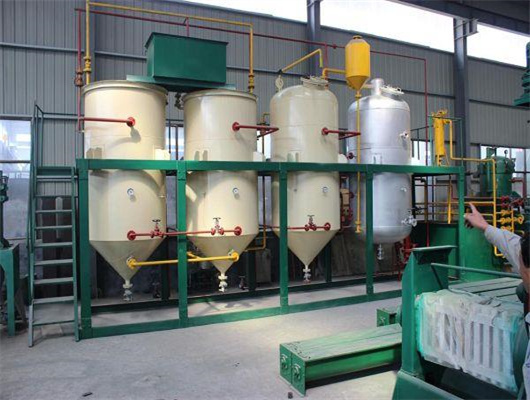
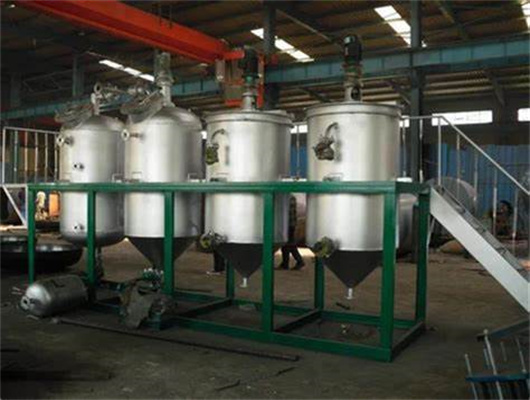
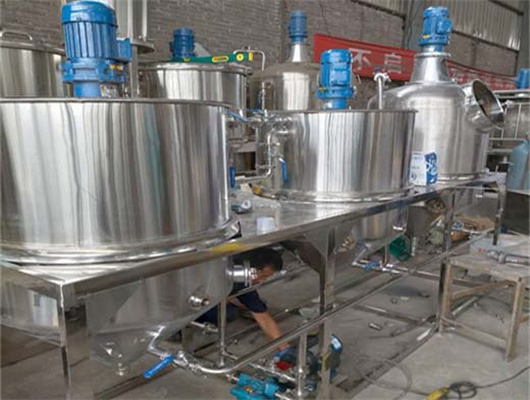
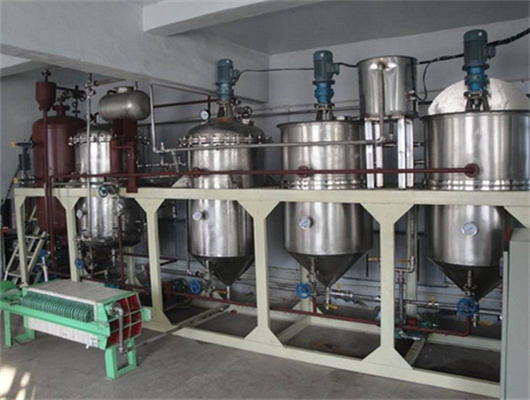
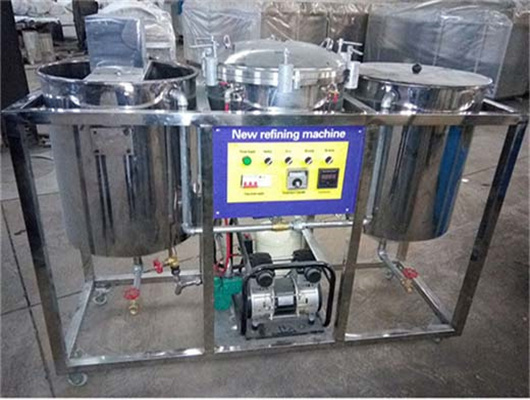
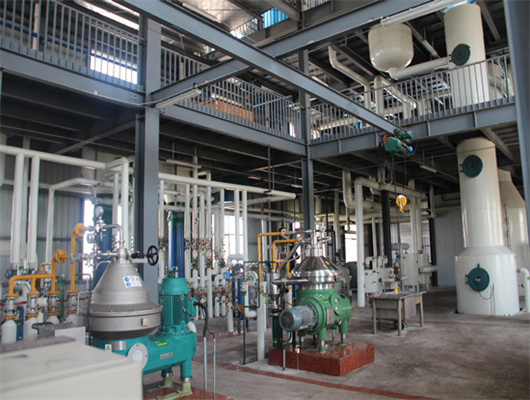
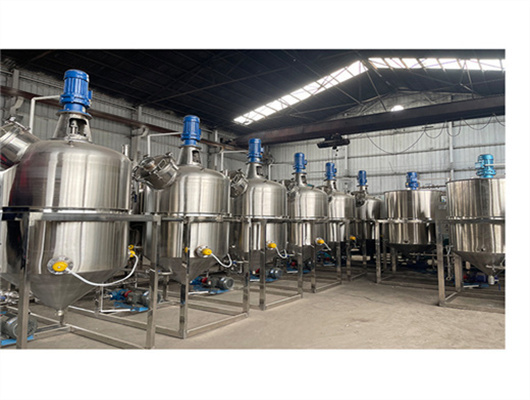
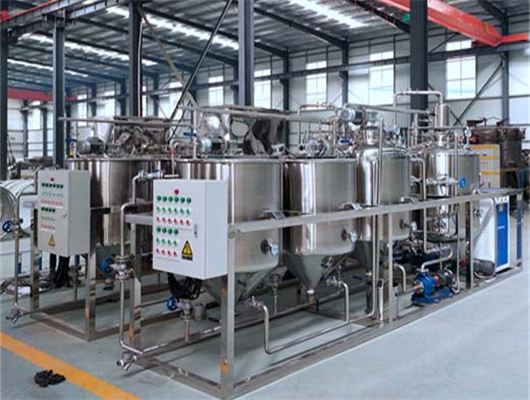
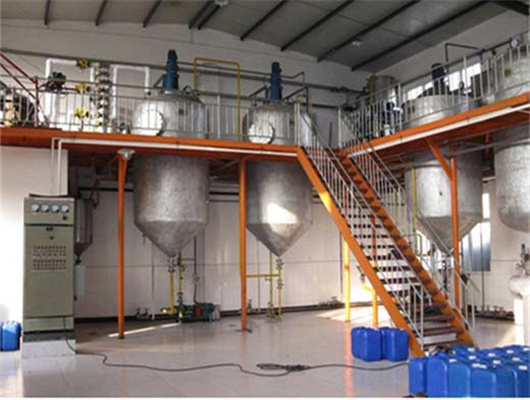
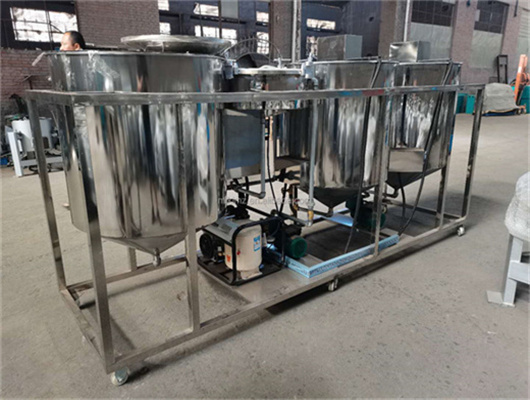
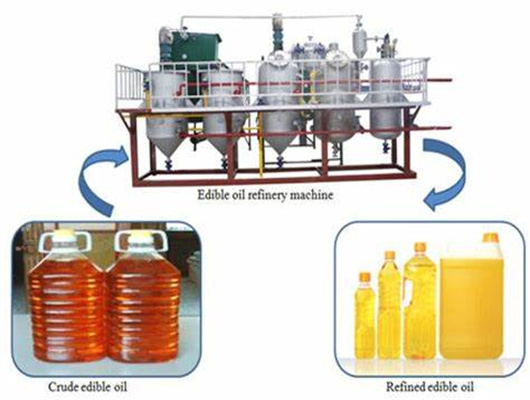
chemical methods peanut oil refinery machine in zambia
- Usage: maize oil refinery
- Type: maize oil refinery
- Automatic Grade: Automatic
- Production Capacity: high
- Model Number: paml oil refinery
- Voltage: 220V, 380V,or other
- Certification: BV, ISO9001, CE, etc...
- phosphoric acid: 2~3kg/T oil
- steam consumption: 450kg/T oil
- certification: BV, ISO9001, CE, etc...
- electric consumption: 28kwh/T oil
- Deodorization loss consumption: ≤0.5%
- Bleaching earth consumption: 5~50Kg/Toil
- Waste bleaching: <35%
- color: depend on the requirements of clients
- capacity: based on the need of clients
Chemical vs. Enzymatic Refining to Produce Peanut Oil for Edible Use
On the other hand, moreover, crude peanut oil and chemically refined peanut oil represent the best solutions for the protection of the grain and to fight S. zeamais in a sustainable and economic way. Further chemical and microscopy investigations could shed light on the mechanism(s) of action that causes the death of S. zeamais when using vegetable oils.
Peanuts, being crucial crops of global importance, have gained widespread recognition for their versatility and nutritional value. In addition to direct consumption, either with or without treatment, peanuts can be the subject of diverse applications focusing mainly on two distinct objectives: oil extraction and defatting processes. As a result of the first process, a solid matrix is generated
Edible Oil Refining Process - Silverson
Edible oil refining is normally a high volume, continuous operation. The reagent additions are traditionally carried out using low shear static mixers or inline agitators, which can lead to several potential problems: The acid and sodium hydroxide solutions make up only a small fraction of the total product, and must be reduced to the smallest
Tocopherol content of fresh oils from runner peanuts has been shown to be minimally affected by O/L ratio (Shin et al. 2009). Copper (Cu) and Iron (Fe) are pro-oxidants present at low levels in seed oils, including peanut. Variation in copper and iron among samples was minimal, ranging from 0.02 to 0.4 ppm for Cu and 0.09 to 0.56 ppm for Fe.
Oils Fats Refining Equipment and Turnkey Plants
We can provide edible oil refining plant equipment with capacity ranging from 50 t/d to 4,000 t/d for soybean oil, rapeseed oil, sunflower seed oil, cottonseed oil, rice bran oil, palm oil, corn oil, peanut oil, linseed oil, animal fats and oils, chicken fat, butter, fish oil and etc. Refining is the last step in edible oil processing.
Among the various existing techniques, enzymatic degumming represents a process that is establishing itself as a valid alternative to the more classic chemical processes. Moreover, vegetable oils of various origins have been gaining more consideration as sustainable and affordable protectants for cereals and pulses against the attack of several insect pests. Sitophilus zeamais (Motschulsky
Edible vegetable oils from oil crops: Preparation, refining
Sunflower oil, soybean oil, palm oil, rapeseed oil and peanut oil are commonly used in cooking [70]. During cooking, oil is added to food to give it taste, colour and fragrance. However, the high temperature and length of the cooking process will not only destroy the unsaturated fatty acids and trace active substances but also lead to the oxidation of the oils into primary or secondary
In 2018, peanut oil sold for US$1470/MT in the United States and for US$1326 in Rotterdam. Peanut oil is recovered primarily by expeller pressing or in combination with hexane extraction. Only four plants process peanut oil in the United States. Peanut oil is processed by conventional caustic refining, adsorbent bleaching, and deodorization.