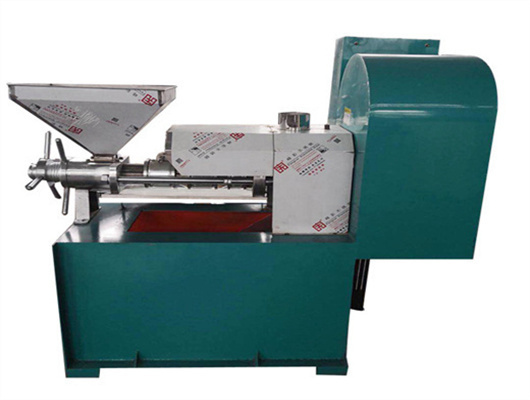
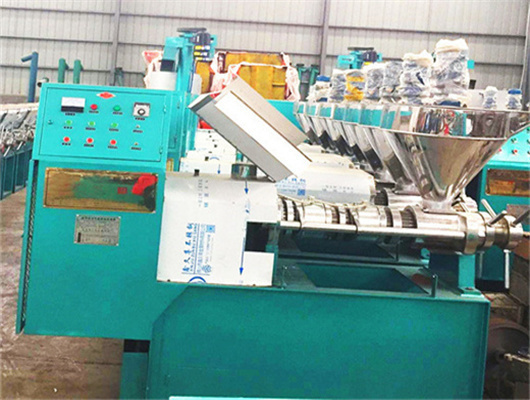
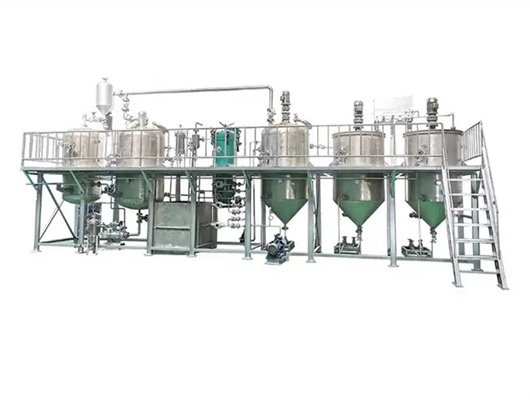
iso ce cooking peanut oil press in botswana
- Usage: Peanut oil processing plant
- Type: Peanut oil processing plant
- Production Capacity: 100%Peanut oil processing plant
- Voltage: 220V/380V/440V
- Power(W): 10-50kw
- Dimension(L*W*H): 1200*400*900mm3
- Weight: According to processing capacity
- Certification: CE ISO BV SGS
- Item: Peanut oil processing plant
- Raw material: Peanut Seed
- Steam pressure: ≥1.2MPa
- Voltatile substance in crude oil: ≤0.3%
- Steam consumption in refining: ≤280kg/ton of oil
- Oil residue in waste clay: ≤25% of waste clay
- Solvent contain in crude oil: ≤200ppm
- Oil residue in meal: <1%
- Warranty: 2years
- Feature: High Oil Yield Efficiency
Production, Processing, and Food Uses of Peanut Oilseed, Oil, and Protein - List - Major Reference Works - Wiley Online Library
Peanut oil is considered as a premium edible oil and commands a high price in both US and European markets. In 2018, peanut oil sold for US$1470/MT in the United States and for US$1326 in Rotterdam. Peanut oil is recovered primarily by expeller pressing or in combination with hexane extraction.
Peanut Oil. Smoke point: Refined peanut oil has a high smoke point of 450°F. Best use: High-heat cooking, especially for stir-frying and deep-frying. Substitutes: Safflower, soybean, or grapeseed oil, which also have high smoke points and a neutral flavor.
Peanut Oil Processing Technology
The conditioned peanut kernels are transported by a conveyor to the twin-screw press for cold pressing; the cold-pressed crude oil and cold-pressed peanut meal with low denaturation will be obtained. After the cold-pressed crude oil is filtered with frame filter, product oil is obtained, which will be packaged by a filling machine to form cold-pressed peanut oil products ( Fig. 3.8 ).
Summary. Peanut oil is a popular cooking oil due to its nutty, mild flavor and high smoke point. It may have several health benefits. It has been linked to lower rates of cardiovascular disease
Physicochemical Characteristics, Functional Properties, and Nutritional Benefits of Peanut Oil: A Review
of peanut oil by an enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction using protease, cellulase, and α -1,4-galacturonide glycanohydrolase either separately or in combination.
In this study, the effect of conventional roasting and the photo-oxidative stability of two cold-pressed peanut oil varieties (Virginia and Valencia) were investigated. Changes in the concentrations of the fatty acids (including trans isomers), minor components, nutritional quality, and antioxidant capacity were analyzed and compared.
How To Use Peanut Oil In Cooking
Peanut oil, also known as groundnut oil, is a popular cooking oil derived from peanuts. It is extracted from the kernels of peanuts through a process of pressing or solvent extraction. With its mild flavor and high smoke point, peanut oil is a versatile choice for various cooking methods.
Peanuts are a relatively high-oil oilseed (with about 50% oil) and the meal after expelling contains about 6–7% oil. Generally the choice peanuts are used as confections (salted whole, in-shell). Lower grade peanuts are crushed for oil and meal. Peanuts like other crops are subject to contamination from aflatoxins.