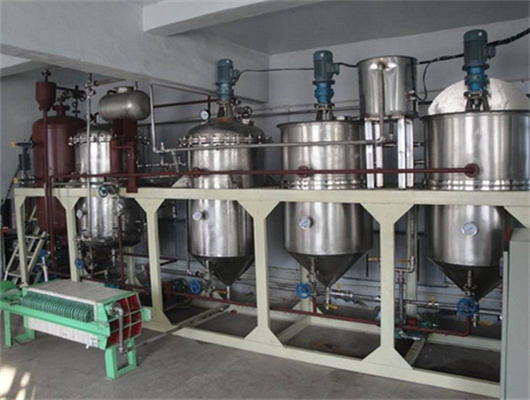
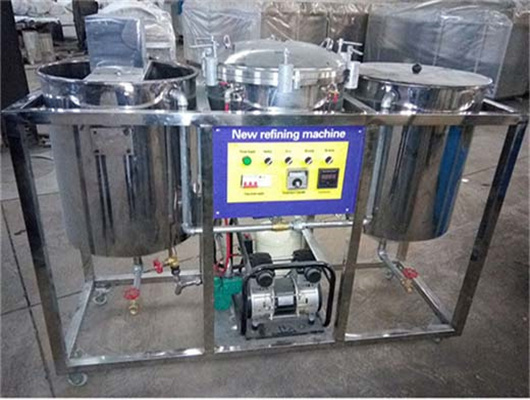
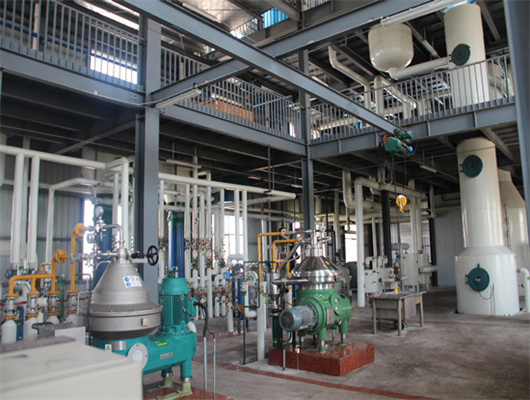
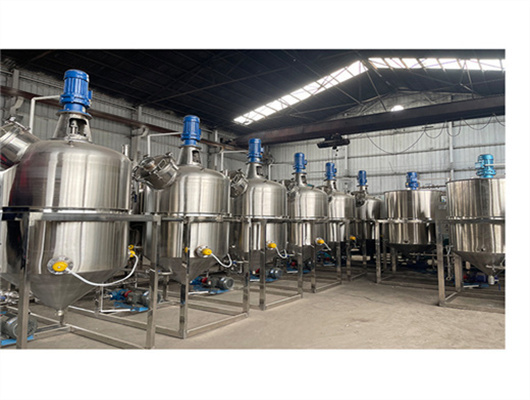
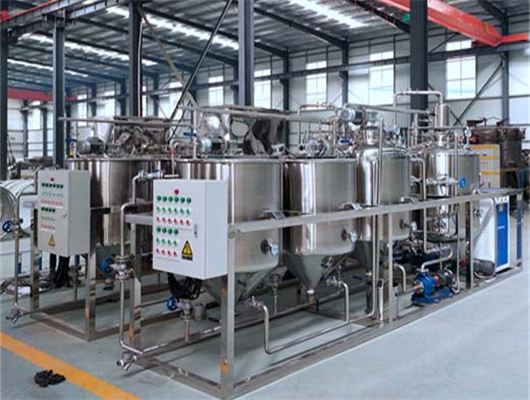
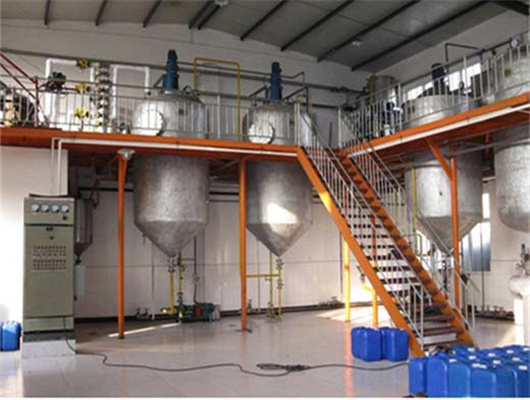
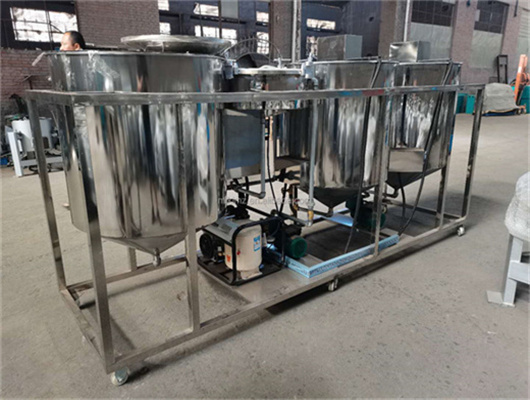
chemical methods peanut oil refinery project in lesotho
- Usage: oil refinery plant
- Type: Sunflower Oil Extraction/Refining Machine
- Automatic Grade: Automatic
- Production Capacity: 1-3000TPD
- Model Number: Sunflower Oil Extraction/Refining Machine
- Voltage: 220V ,380V
- Power(W): According to your capacity
- Dimension(L*W*H): 48m*12M*15M(30TPD)
- Weight: 30tons
- Certification: CE,BV & ISO9001
- usage: Sunflower Oil Extraction/Refining Machine
- features: high output, good quality
- aim: provide the best quality and realible product for you
- product: reach to the national oil standard
- type: Sunflower Oil Extraction/Refining Machine
- moisture and volatile matter(%): less than 0.05
- insoluble impurity(%): less than 0.05
- residual solvent content in oil: no
- smoking point: higher than 215 degree
- Residual solvent in finished meal: less than 300PPM
Effect of Industrial Chemical Refining on the - Springer
The effect of the industrial chemical refining process on the physicochemical properties, fatty acid composition, and bioactive minor components of peanut oil was studied. The results showed that the moisture and volatile matter content, acid value, peroxide value, and p-anisidine value were significantly changed (P 0.
Fate of AFB 1 during peanut oil refining. The crude peanut oil was fortified with a relatively high concentration of AFB 1 stock solution at the final concentration of 500 μg/kg AFB 1. A laboratory simulation of the refining process, including the oil degumming, deacidification, and decolorization phases, was conducted to investigate the
Chemical vs. Enzymatic Refining to Produce Peanut Oil for Edible Use
Regarding the toxicity towards S. zeamais, the crude peanut oil and the chemically refined peanut oil had lower LC 50 values (1.836 and 1.372 g kg −1, respectively) than the oils rectified through enzymatic degumming (LC 50 from 2.453 to 4.076 g kg −1), and, therefore, they can be suggested as sustainable stored grain protectants.
Tocopherol content of fresh oils from runner peanuts has been shown to be minimally affected by O/L ratio (Shin et al. 2009). Copper (Cu) and Iron (Fe) are pro-oxidants present at low levels in seed oils, including peanut. Variation in copper and iron among samples was minimal, ranging from 0.02 to 0.4 ppm for Cu and 0.09 to 0.56 ppm for Fe.
Defatting and Defatted Peanuts: A Critical Review on Methods of Oil
Peanuts, being crucial crops of global importance, have gained widespread recognition for their versatility and nutritional value. In addition to direct consumption, either with or without treatment, peanuts can be the subject of diverse applications focusing mainly on two distinct objectives: oil extraction and defatting processes. As a result of the first process, a solid matrix is generated
In 2018, peanut oil sold for US$1470/MT in the United States and for US$1326 in Rotterdam. Peanut oil is recovered primarily by expeller pressing or in combination with hexane extraction. Only four plants process peanut oil in the United States. Peanut oil is processed by conventional caustic refining, adsorbent bleaching, and deodorization.
Edible vegetable oils from oil crops: Preparation, refining
Sunflower oil, soybean oil, palm oil, rapeseed oil and peanut oil are commonly used in cooking [70]. During cooking, oil is added to food to give it taste, colour and fragrance. However, the high temperature and length of the cooking process will not only destroy the unsaturated fatty acids and trace active substances but also lead to the oxidation of the oils into primary or secondary
Among the various existing techniques, enzymatic degumming represents a process that is establishing itself as a valid alternative to the more classic chemical processes. Moreover, vegetable oils of various origins have been gaining more consideration as sustainable and affordable protectants for cereals and pulses against the attack of several insect pests. Sitophilus zeamais (Motschulsky
- What is petroleum refinery and petrochemical plants (PRPP)?
- Petroleum refinery and petrochemical plants (PRPP) are a group of industries that deal with the production of fuels, lubricants, petrochemicals, and their intermediates. The global economic development and increase in population have created a considerable demand for PRPP products.
- What is the production capacity of refined edible oil?
- Abstract :- Industry manufacturing refined edible oil with a capacity of 18000 tones/annum generated wastewaters and solid waste ( chemical and biological sludges). During production of edible oil , different THE REFINING OF CRUDE EDIBLE OILS GENERATES LARGE AMOUNTS OF WASTEWATER. THE
- How is peanut oil processed?
- Only four plants process peanut oil in the United States. Peanut oil is processed by conventional caustic refining, adsorbent bleaching, and deodorization. The food uses of peanut oil and protein are reviewed in this article. Abstract This article reviews the production, processing, and food uses of peanut oil and protein.
- What is waste from edible oil refinery?
- The waste from edible oil refinery included solid wastes viz. spent earth, chemical and biological sludge and wastewater from soap splitting unit, floor washing, and cooling and boiler sections. The combined wastewater from soap splitting and floor washing had high concentration of oil and COD.