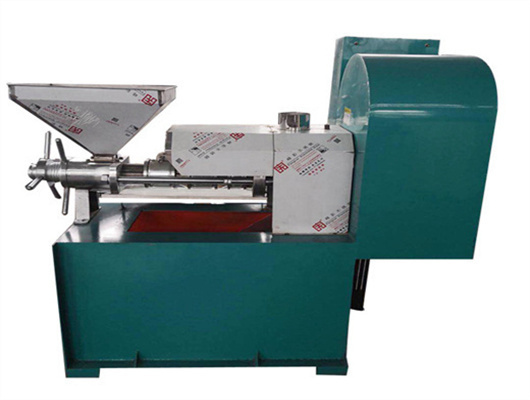
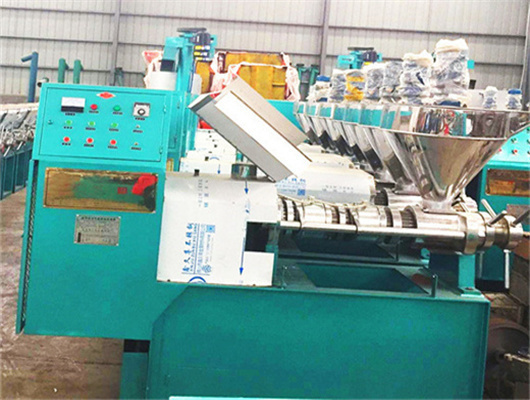
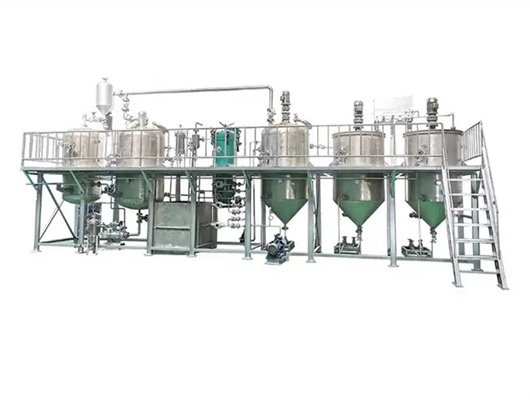
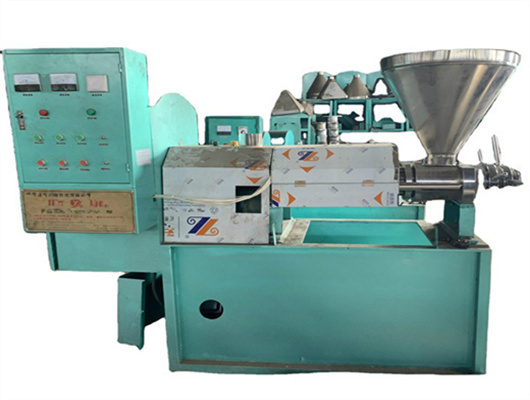
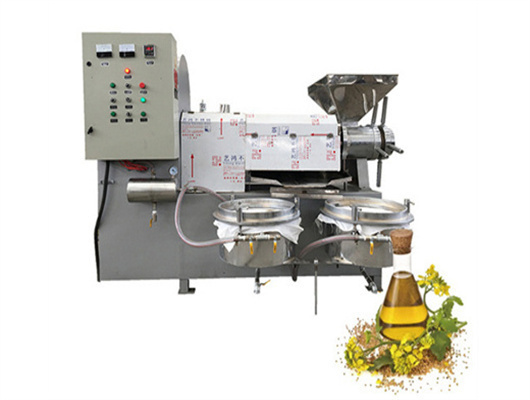
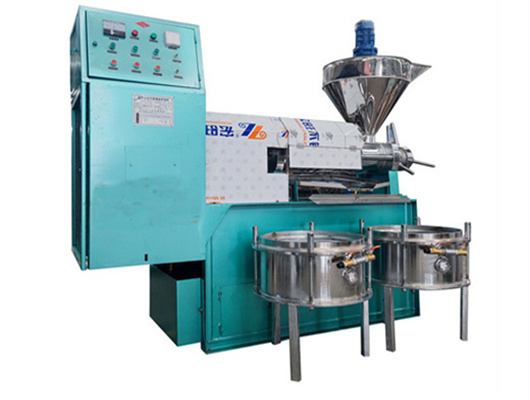
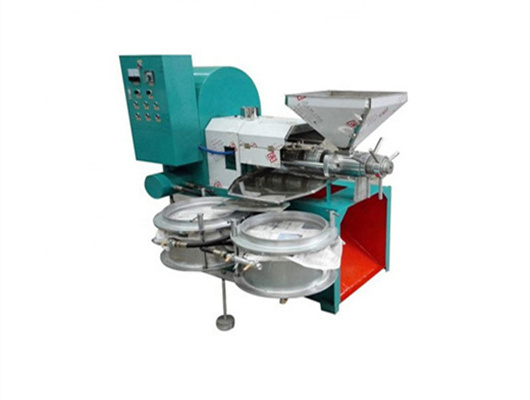
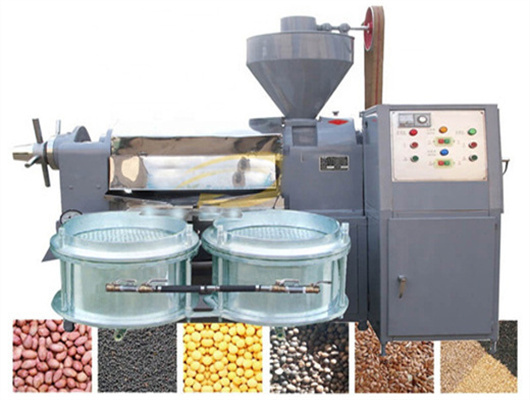
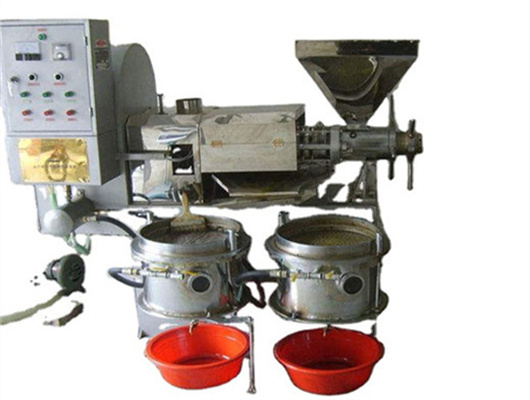
inca peanut oil presss in ethiopia
- Usage: Peanut Oil
- Type: edible oil solvent extraction machine, Peanut oil extraction plant
- Production Capacity: 100 kg/h - 1000kg/h
- Voltage: Local Voltage
- Power(W): Capacity
- Dimension(L*W*H): 1200*400*900mm3
- Certification: CE ISO
- Oil residue ratio: 0.5-1%
- Solvent consumption: ≤ 2Kg/T (No.6 solvent oil)
- Power consumption: ≤ 15KWh/T
- Steam consumption: ≤ 280KG/T (0.8MPa)
- Residual oil in meal: ≤ 1% (Peanut)
- Crude oil moisture and volatile matter: ≤ 0.30%
- Finished meal moisture: ≤ 13% (adjustable)
- Price: Competitive
- Quality: Top Level
AMINO-ACID AND FATTY-ACID PROFILES OF THE INCA PEANUT (PLUKENETIA-VOLUBILIS) - Semantic Scholar
The Inca peanut (IP), Plukenetia volubilis, is a potential new crop indigenous to the high-altitude rain forests of the Andean region of South America and produces seeds that have a nutlike appearance and contain high amounts of oil and protein. The Inca peanut (IP), Plukenetia volubilis, is a potential new crop indigenous to the high-altitude rain forests of the Andean region of South America
The variety volubilis means “circling, revolving”, indicating that it is a climbing plant. Sacha inchi is a perennial, perfect plant with hairy, heart-shaped leaves. The upper side of the leaves is shiny and deep green, the leaf edge is serrated. The leaves are 10–12 cm long and 8–10 cm broad; the leaf stem is 2–6 cm long.
Safety assessment of Plukenetia volubilis (Inca peanut) seeds, leaves, and their products - Srichamnong - 2018 - Food Science & Nutrition - Wiley
Furthermore, Inca peanut oil has the highest amount of ω-6 compared to olive, soy, maize, and sunflower oils (Hanssen & Schmitz-Hübsch, 2011). It has been proven that Inca peanut oil is not only safe but also could increase HDL cholesterol in humans (Gonzales & Gonzales, 2014 ).
Peanut Production. 2022 Long Rains (Mar - Dec) — (Last Chart Updated on 04/30/2024) Subregions: Primary Production in Ethiopia. (~80% of total peanut production) Oromia. (55% of total peanut production) Benshangul-Gumaz. (18% of total peanut production)
Structural, functional properties and immunomodulatory activity of isolated Inca peanut
Inca peanut, a promising new crop, is now widely cultivated in many other countries, including Colombia and Thailand; and it was introduced to China in 2006. It has recently attracted considerable interest because of its high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acid and vitamin E levels and potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries [1].
Plukenetia volubilis, commonly known as sacha inchi, sacha peanut, mountain peanut, Inca nut or Inca-peanut, is a perennial plant in the family Euphorbiaceae, having small trichomes on its leaves. It is native to much of tropical South America ( Suriname , Venezuela , Bolivia , Colombia , Ecuador , Peru , and northwestern Brazil ), as well as some of the Windward Islands in the Caribbean . [2]
Effect of different valence metal cations on the gel characteristics and microstructure of Inca peanut albumin gels
Inca peanut is primarily an excellent oil crop and the oil extracted has a high polyunsaturated fatty acid content (90%). Due to the rising demand for Inca peanut oil on the market, large quantities of Inca peanut meal containing nutritive protein (59.1%) are generated as a by-product.
Abstract The Inca peanut (IP), Plukenetia volubilis, is a potential new crop indigenous to the high-altitude rain forests of the Andean region of South America. It grows as a vine and produces seeds that have a nutlike appearance and contain high amounts of oil (54%) and protein (27%).
- How is Sacha Inchi oil extracted?
- The harvest is still, however, manual (Hanssen and Schmitz-Hübsch 2011; Pies 2010, p. 7, 10, 11, 16). Sacha inchi oil is usually cold pressed. Another possibility is extraction with solvents or supercritical carbon dioxide. Pressing is preferable because it is an environment-friendly method and results in high-quality oil.
- Is Sacha Inchi a Peruvian seed?
- Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis Linneo, Euphorbiaceae) is known as a Peruvian seed containing a high level of unsaturated fatty acids, such as ¦Á-linolenic acid (Omega-3), linoleic acid (Omega-6),¡ … …
- What is Inca peanut?
- Plukenetia volubilis or Sacha inchi, the Inca peanut, is a tropical plant from the Euphorbiaceae family of the Amazon region (Gillespie, 1993 ). At present, the seeds have been utilized primarily for oil production. Besides, the boiled or roasted seeds and leaves are also edible (Hamaker et al., 1992 ).
- What are the health risks of eating Inca peanuts?
- Fresh Inca peanut seeds (FS) and leaves (FL) contain various levels of heat-labile phytotoxins, including alkaloids, saponins, and lectins. High and chronic consumption of FS and FL should be of concern in order to reduce hazard risks.