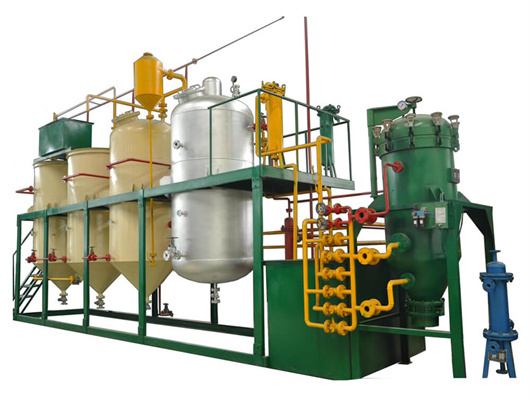
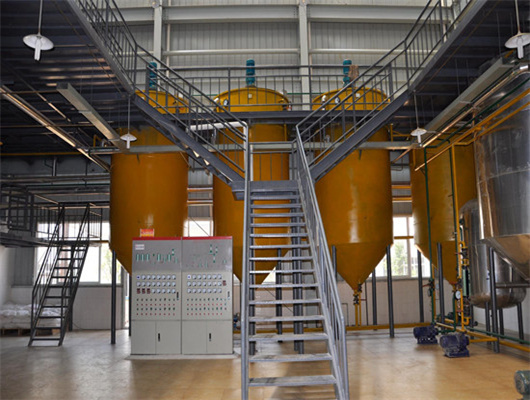
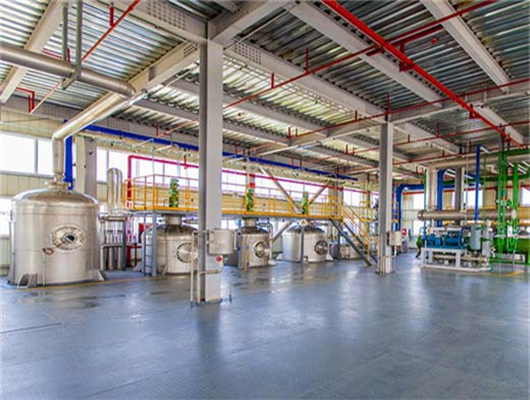
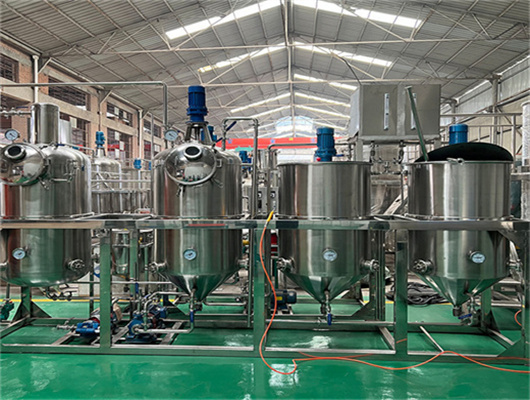
peanut pumpkin seeds oil refinery refining market in congo
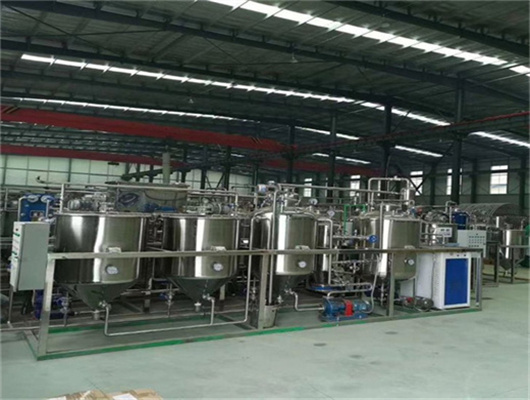
- Type: oil deodorization equipments for plant
- Use: oil refining
- Certification: ISO CE BV
- Model Number: oil deodorization equipments for plant
- Product type: oil deodorization equipments for plant
- Bleaching earth consumption: 3-5Kg/T oil
- Deodorization loss consumption: ≤0.5%
- Circulating water cooling water yield: 150M3/H
- Phosphoric acid: 2~3 kg/T oil
- Alkali: acid valuex1-3kg/T oil
- Water(soften water): 150Kg/T oil
- Steam consumption: 700KG/T oil
- Bleaching losses: the quantity of bleaching earth multiplys 0.25%
- Electric consumption: 28Kwh/T oil
Refinery profile: Pointe Noire II cracking refinery, Congo
Subsequent expansion at the Pointe Noire II cracking refinery will increase its refining capacity by 60mbd. Contractors involved in the refinery Some of the key contractors for the upcoming projects at the Pointe Noire II cracking refinery include the following. Main EPC: China National Chemical Engineering Group. About Atlantic Petrochemical
April 15, 2024. The Republic of the Congo’s national oil company (NOC) the Société Nationale des Pétroles du Congo and the State Oil Company of Azerbaijan ( SOCAR) signed three agreements of cooperation in the fields of refinery development, training and sustainable natural resource management. An MoU on terms for the improvement and
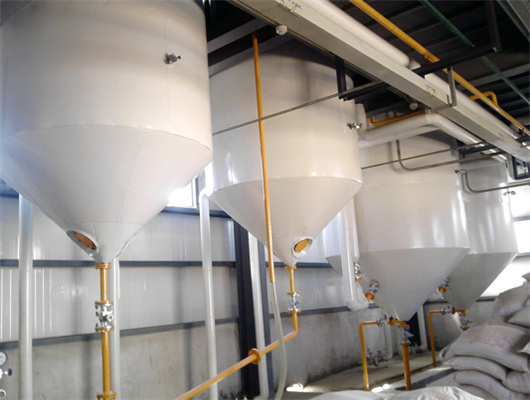
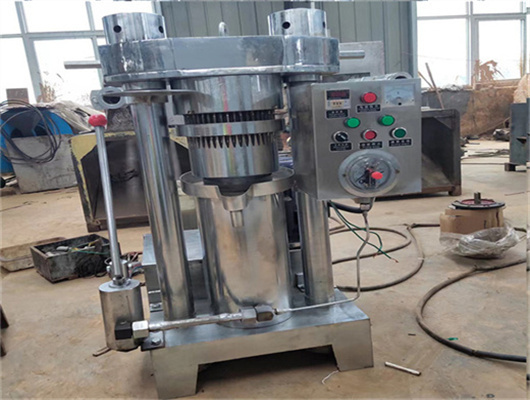
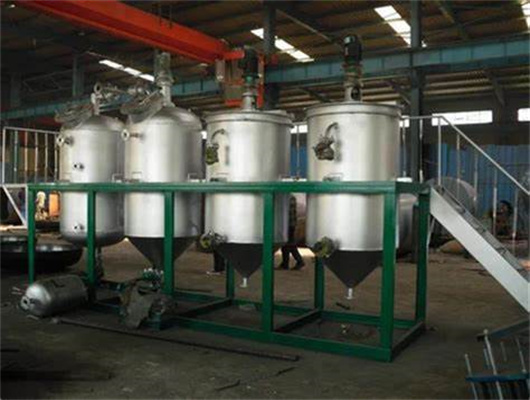
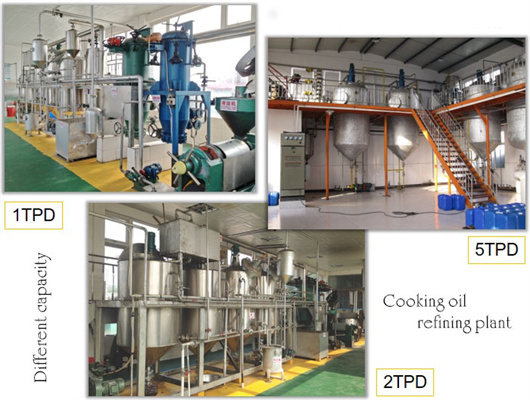
20-2000t pumpkin seeds oil refinery machine
1. Oil seeds: We can provide machine to process various oil seeds, such as peanut, soybean, sunflower, coconut, colza, mustard, palm rapeseed and so on. 2. Magnetic box: Clearing the iron impurity which might be in the oil seeds. The iron impurity will be harmful to the following machines, so we need take the iron impurities out. 3.
We can provide edible oil refining plant equipment with capacity ranging from 50 t/d to 4,000 t/d for soybean oil, rapeseed oil, sunflower seed oil, cottonseed oil, rice bran oil, palm oil, corn oil, peanut oil, linseed oil, animal fats and oils, chicken fat, butter, fish oil and etc. Refining is the last step in edible oil processing.
Republic of the Congo Launches Construction of $600-Million
The Republic of the Congo launched the construction of a $600-million oil refinery near the port city of Pointe-Noire on Sunday. The ground-breaking ceremony was attended by President Denis Sassou Nguesso and represented as a pivotal moment for the nation’s hydrocarbon sector, which seeks to increase domestic refining capacity and offset chronic fuel shortages.
The country’s first refinery, the Congolaise de raffinage (Coraf), has been in operation since 1982. The refinery has the capacity to process 1 million tons of oil per year, but officially only processes 600,000 tons annually. The country’s needs are estimated at 1.2 million tons. While Congo-Brazzaville is currently the fourth-largest oil
Congo annuls first gold refinery permit days before inauguration
Credit: Congo Gold Raffinerie Sarl. The Democratic Republic of Congo’s government revoked its authorization for the country’s first gold refinery, days before its planned inauguration on
Edible Oil Plant | GFIPL. GFIPL edible oil division is engaged in manufacturing edible oil by solvent extraction and refining processes. This unit was set up in 2003 with an initial production capacity to the tune of 250 MT/day of crushing capacity and 100 MT/day of refi
- What is the main resource sector in Congo?
- Oil and Gas dominates the resource sector of the Republic of the Congo ( French: République du Congo ), also referred to as Congo-Brazzaville, with the petroleum industry accounting for 89% of the country’s exports in 2010.
- How much petroleum does Congo export?
- Nearly all of the country’s hydrocarbons were produced off-shore. According to the OPEC annual statistical bulletin of 2022, the Congo exported $5,785 billion worth of petroleum in 2021. This accounts for 79.3% of its net exports of $7,291 billion.
- What is Congo’s first oil refinery?
- The country¡¯s first refinery, the Congolaise de raffinage (Coraf), has been in operation since 1982. The refinery has the capacity to process 1 million tons of oil per year, but officially only processes 600,000 tons annually. The country¡¯s needs are estimated at 1.2 million tons.
- What happened to oil production in Congo?
- By the turn of the century, production began to decline as existing oil fields reached maturity. As of 2008, oil production has increased every year as a result of several new projects, mainly Congo’s first deep-water field Moho-Bilondo. The Congo is the sixth largest oil producer in sub-Saharan Africa.