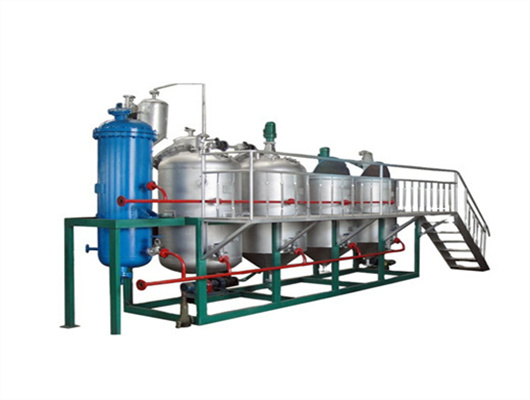
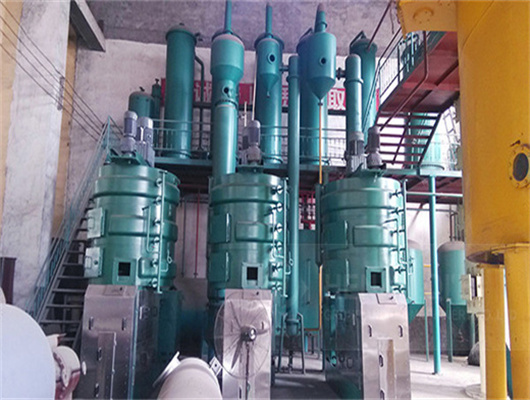
soybean moisture content for oil extraction in lesotho
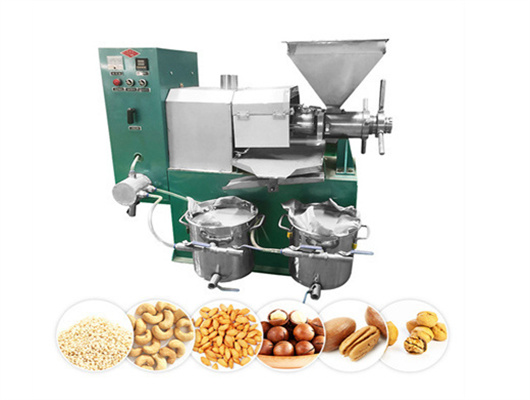
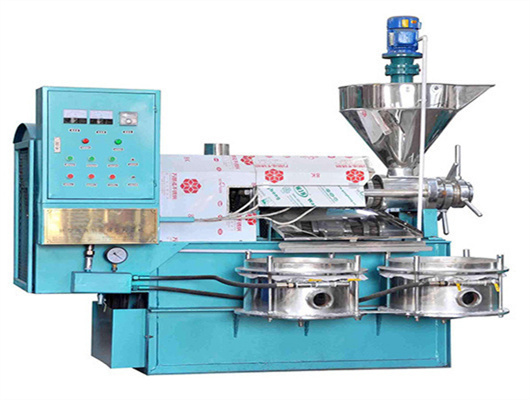
- Usage: Vegetable Oil
- Production Capacity: 35-80T/D
- Voltage: 380V
- Dimension(L*W*H): 2900X1850X3240m
- Weight: 5000Kg
- Core Components: Motor, Pressure vessel, Pump, Engine
- Oil type: Soybean Oil
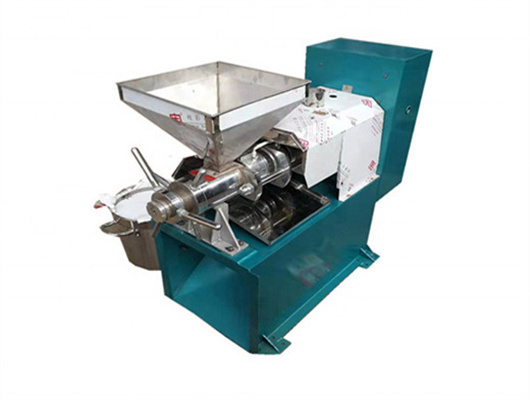
- Product Name: screw oil press
- Processing Method: Hot/Cold Pressed Method
- Material: Q235
- Advantage: High Oil Yield
- Capacity: 40t/d
- After Warranty Service: Video technical support, Online support
- Local Service Location: Egypt, Viet Nam, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, South Africa, Kazakhstan, Nigeria, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan
- Certification: SGS ISO
Effect of Moisture Content on the Quality of Soybean Oil and Meal
Soyflakes and soybrokens having 8% to 16% wet basis (w.b.) moisture contents were extracted for 8h (about 50% extraction) using the azeotrope (91%) of isopropyl alcohol (IPA) at 7.75ml/min flow rate.
However, the pattern of moisture content was consistent with [13] who reported that oil extracted from seed having 8.4% moisture content on wet basis was considered to be of good quality with a
Soybean oil bodies: A review on composition, properties, food
The oil content of the plant material could influence OBs formation, and their size during biogenesis. For example, peanut and sesame seeds have higher oil content than soybean (Deng et al., 2018; Pathak, Rai, Kumari, & Bhat, 2014), although peanut/sesame seed OBs are larger and the ratio of oil to protein is higher (Table 1).
Soybean oil is the 2nd most consumed oil (28%) [1], being widely employed in the food industry and in homemade foods [3], being also one of the lipidic material mostly used for biodiesel production worldwide [4]. Due to the moderate oil content (18 – 23%mass) [5], it is mandatorily recovered from soybeans by solvent extraction [6].
Characterization and Optimization of Soybean Oil from Soybean
The soybean seed oil was extracted from of 0.25 mm, moisture content of 12-13%, temperature of 69°C and the extraction time . between 3.5 an d 4.5 hrs gave the maximum oil yield.
Soyflakes and soybrokens having 8% to 16% wet basis (w.b.) moisture contents were extracted for 8 h (about 50% extraction) using the azeotrope (91%) of isopropyl alcohol (IPA) at 7.75 ml/min flow rate. The moisture contents of soyflakes and soybrokens significantly affected oil recovery with IPA. Regression analysis was performed to optimize moisture contents of soyflakes and soybrokens during
Flaking as a Pretreatment for Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction
Soybean moisture content (7.2–12.8%) and conditioning temperature (51–79 °C) during flaking were evaluated to determine their effects on oil and protein extraction and oil distribution among fractions produced in enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction processing (EAEP). Extractions were performed by using two-stage countercurrent EAEP at a 1:6 solids-to-liquid ratio with 0.5% protease (wt/g
The extraction of soybean oil and free fatty acids was evaluated using ethanol with different hydration levels (from anhydrous to 5.98 wt%) by Toda et al. [29]. It was found that the increase in water content suppresses soybean oil extraction and increases the free fatty acids content.
- Which solvent is used in soybean oil production?
- Solvent extraction and expelling are the main processes used in soybean oil production. Hexane is currently the leading solvent in extraction , . This solvent has a high solubility for oil extraction, availability, low price, low boiling point, and heat of vaporization .
- How to extract soybean oil?
- Soybean oil can be obtained by expelling or using an organic solvent. Although, the employment of solvent will always follow the expelling to increase lipid extraction yield .
- How to detect soybean oil and moisture content?
- Soxhlet extraction, oven drying, LF-NMR spectrum, and LF-NMR oil and moisture content software were used to detect soybean oil and moisture content. The comparison showed that the LF-NMR oil and moisture content software was faster and more accurate than the other methods.
- What is the moisture content of soybean oil?
- Usually in soy oil industry, soybeans with initial moisture contents of 11¨C15% w.b. are dried in the temperature range of 70¨C93°C to reduce the moisture content to 9¨C10% w.b. At this moisture level, reduced viscoelastic stress development produces thin flakes desirable for oil extraction (Singh et al. 2004 ).