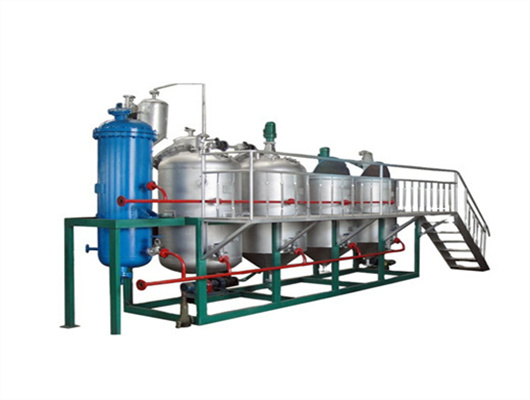
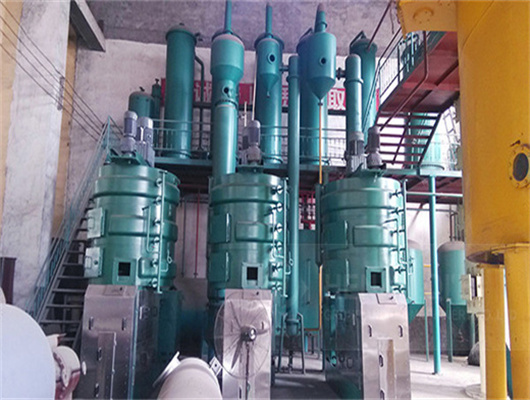
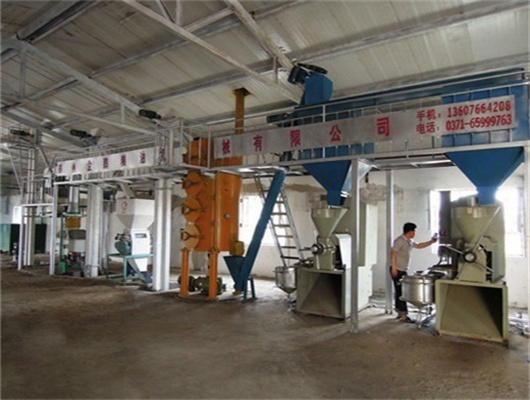
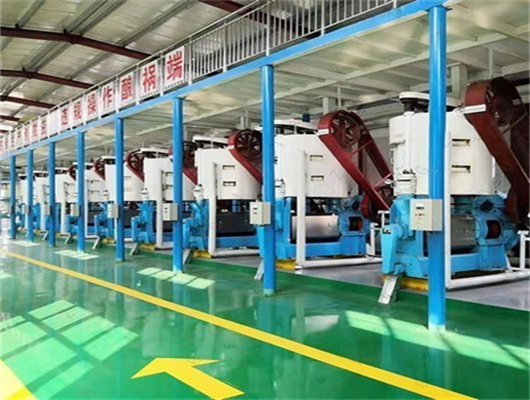
oil extraction peanut soybean in togo
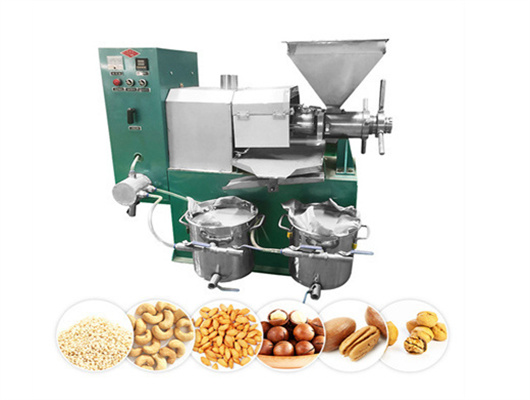
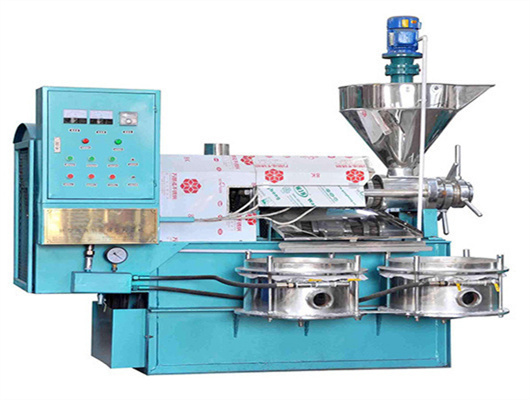
- Usage: Peanut , Peanut oil edible oil
- Production Capacity: 9-11 Tons per day
- Voltage: 220V/380V/440V
- Dimension(L*W*H): 2850*1850*3270mm(depend on capacity)
- Weight: 5000 kg(depend on capacity)
- Core Components: Motor
- Item: Peanut oil making machinery
- Capacity: 10t/d, 20t/d, 30t/d, 40t/d, 50t/d, 60t/d, 70t/d, 80t/d,100t/d, 150t/d
- residual oil rate: ≥ 97%, meal residual: ≤ 1%, press cpress cake residual: ≤ 6%
- processing steps: pretreatement, extracting, cleaning
- Raw material: carbon steel & stainless steel
- Color: Clients' Requirements
- Advantage: full automatic, high efficiency, energy saving
- Function: oil press
- After Warranty Service: Online support
- Certification: ISO CE
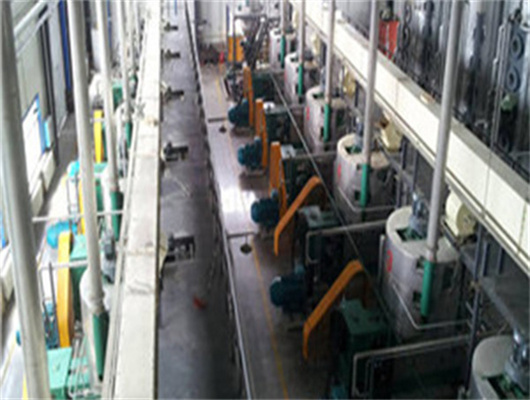
Peanut Soybean Oil Production Line Set up in Togo | Project
The main oil crops in Togo is peanut, cotton seed, oil palm, soybean and more. But, the edible oil production industry in Togo is relatively small and its consumption of cooking oil is increasing in these years. So, it is a great opportunity to setup a cooking oil production plant in Togo to get more profits.
Oilseeds are crucial for the nutritional security of the global population. The conventional technology used for oil extraction from oilseeds is by solvent extraction. In solvent extraction, n-hexane is used as a solvent for its attributes such as simple recovery, non-polar nature, low latent heat of vaporization (330 kJ/kg) and high selectivity to solvents. However, usage of hexane as a
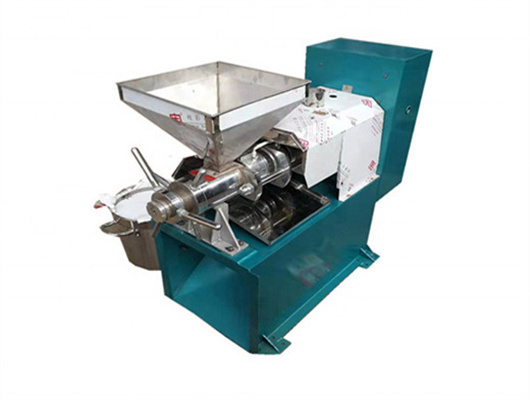
10TPD Soya / Peanut Oil Producing Plant in Togo
Water content: 5 – 10 %; temperature: 105 – 110 degrees; Requiring Time: 60mins. Oil Pressing process: After preprocessing, the soybean and peanut are ready for oil expelling. Filtering oil: Filtering the crude oil with oil-dreg sieves, which run reposefully, less malfunction, less occupying area, it’s the better oil-dreg separator, then
The three major steps involved in solvent extraction are oilseed cleaning and conditioning, oil extraction, and separation of the miscella. Crude oil and meal quality depend mostly on type of solvent used, reaction temperature, and type of pretreatment given to the oilseed [ 25, 26 ].
Optimization of antioxidants extraction from peanut skin
However, Yadav, Yogesh, and Aswani (2014) using a methanolic PSE at a level 10 times higher (0.5%) found similar activity that BHT during accelerated storage of soybean oil at 65 °C for seven days. Duh and Yen (1997) also reported similar antioxidant activity of methanolic extract from peanut hulls in soybean oil. Hence, our results showed
Abstract. As naturally sourced proteins, peanut proteins have garnered significant attention from the food industry, owing to their numerous advantages, such as easy extraction, non-pungency, and high bioavailability. Furthermore, peanut proteins are highly digestible in the gastrointestinal tract and boast a high net protein utilization rate
Peanut oil and protein extraction using an aqueous enzymatic
Following new method, highest yields obtained for oil and protein were 95.48% and 80.74%, respectively. The new method reduced the conditions of enzymatic hydrolysis and accelerated the demulsification of emulsions. Significance and Novelty. The study provides a two-step aqueous enzymatic method for extracting emulsions and proteins from peanut.
For instance, a low yield of oil was observed in soybean, rapeseed, peanut and sunflower due to low solubility of protein at isoelectric point [35, 36]. To corroborate further, flaxseed oil yield was higher when treated with mixture of enzymes (cellulase, hemicellulase and pectinase, at a ratio of 1:1:1) at pH 4.5–5.0 than treatment with